INDEPENDENT AUDITOR’S REPORT
Report on the Audit of the Financial Statements – GAJMA & CO, Chartered Accountants Colombo.
July 27, 2023
Opinion
We have audited the financial statements of Kuruganga Hydro (Private) Limited (the Company), which comprise the statement of financial position as at March 31, 2023, and the statement of comprehensive income, statement of changes in equity and statement of cash flows for the year then ended, and notes to the financial statements, including a summary of significant accounting policies.
In our opinion, the accompanying financial statements give a true and fair view of the financial position of the Company as at March 31, 2023, and of its financial performance and its cash flows for the year then ended in accordance with Sri Lanka Accounting Standard for Small and Medium-Sized Entities (SLFRS for SMEs).
Basis for Opinion
We conducted our audit in accordance with Sri Lanka Auditing Standards (SLAuSs). Our responsibilities under those standards are further described in the Auditors Responsibilities for the Audit of the Financial Statements section of our report. We are independent of the Company in accordance with the ethical requirements of the Code of Ethics issued by CA Sri Lanka (Code of Ethics) that are relevant to our audit of the financial statements, and we have fulfilled our other ethical responsibilities in accordance with the Code of Ethics. We believe that the audit evidence we have obtained is sufficient and appropriate to provide a basis for our opinion.
Responsibilities of Management and Those Charged with Governance for the Financial Statements
Management is responsible for the preparation of financial statements that give a true and fair view in accordance with SLFRS for SMEs, and for such internal control as management determines is necessary to enable the preparation of financial statements that are free from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error.
In preparing the financial statements, management is responsible for assessing the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern, disclosing, as applicable, matters related to going concern and using the going concern basis of accounting unless management either intends to liquidate the Company or to cease operations, or has no realistic alternative but to do so.
Those charged with governance are responsible for overseeing the Company’s financial reporting process. Auditor’s Responsibilities for the Audit of the Financial Statements
Our objectives are to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements as a whole are free from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error, and to issue an auditor’s report that includes our opinion. Reasonable assurance is a high level of assurance but is not a guarantee that an audit conducted in accordance with SLAuSs will always detect a material misstatement when it exists. Misstatements can arise from fraud or error and are considered material if, individually or in the aggregate, they could reasonably be expected to influence the economic decisions of users taken on the basis of these financial statements.
As part of an audit in accordance with SLAuSs, we exercise professional judgment and maintain professional skepticism throughout the audit. We also:
- Identify and assess the risk of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to fraud or error, design and perform audit procedures responsive to those risks, and obtain audit evidence that is sufficient and appropriate to provide a basis for our opinion. The risk of not detecting a material misstatement resulting from fraud is higher than for one resulting from error, as fraud may involve collusion, forgery, intentional omissions, misrepresentations, or the override of internal control.
- Obtain an understanding of internal control relevant to the audit in order to design audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control.
- Evaluate the appropriateness of accounting policies used and the reasonableness of accounting estimates and related disclosures made by management.
- Conclude on the appropriateness of management’s use of the going concern basis of accounting and, based on the audit evidence obtained, whether a material uncertainty exists related to events or conditions that may cast significant doubt on the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. If we conclude that a material uncertainty exists, we are required to draw attention in our auditor’s report to the related disclosures in the financial statements or, if such disclosures are inadequate, to modify our opinion. Our conclusions are based on the audit evidence obtained up to the date of our auditor’s report. However, future events or conditions may cause the Company to cease to continue as a going concern.
- Evaluate the overall presentation, structure and content of the financial statements, including the disclosures, and whether the financial statements represent the underlying transactions and events in a manner that achieves fair presentation.
We communicate with those charged with governance regarding, among other matters, the planned scope and timing of the audit and significant audit findings, including any significant deficiencies in internal control that we identify during our audit.
Report on Other Legal and Regulatory Requirements
As required by section 163 (2) of the Companies Act No. 07 of 2007, we have obtained all the information and explanations that were required for the audit and, as far as appears from our examination, proper accounting records have been kept by the Company.



Accounting policies and explanatory notes to the financial statements for the year ended March 31, 2023
- GENERAL INFORMATION
- Domicile and Legal Form
Kuruganga Hydro (Private) Limited is a limited liability Company, incorporated and domiciled in Sri Lanka under the Companies Act, No. 7 of 2007. The registered office of the Company and its principal place of business is situated at No. 129/7A, Duwa Road, Baddegana, Pita Kotte. The Company was incorporated on April 23, 2014. - Principal Activity and Nature of Operations
The principal activity of the Company is to carry on the business of operating a mini hydro power plant to generate and supply of electricity to the national grid. - Parent Entity
The Company’s parent undertaking is Pacific Million Care Ltd since February 15, 2019, a Company incorporated in Hong Kong. - Approval of Financial Statements
These financial statements were approved by the Board of Directors and authorized for issue on July 27, 2023.
- Domicile and Legal Form
- BASIS OF PREPARATION
- Statement of Compliance
The statement of financial position, statement of comprehensive income, statement of changes in equity, statement of cash flows and notes relevant to the financial statements of the Company have been prepared in accordance with the Sri Lanka Accounting Standard for Small and Medium-Sized Entities (SLFRS for SMEs) issued by the Institute of Chartei.ed Accountants of Sri Lanka and in compliance with the requirements of the Companies Act, No. 7 of 2007. - Basis of Measurement
Financial statements of the company are prepared under the historical cost convention. Adjustments have not been made for inflationary factors affecting the financial statements. - Going Concern
The directors have made an assessment of the company’s ability to continue as a going concern and they do not intend either to liquidate or to cease operations of the Company in foreseeable future. - Comparative Figures
The previous year figures and phrases have been reclassified whenever necessary to conform to the current year presentation. - Functional and Presentation Currency
Items included in the financial statements of the Company are measured using the currency of the primary economic environment in which the Company operates (the functional currency) and rounded to the nearest rupee value.
These financial statements are presented in Sri Lankan Rupees (Rs.) which is the Company’s functional and presentation currency. - Use of Estimates and Judgments
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with the SLFRS for SMEs requires the management to make judgments, estimates and assumptions that affect the application of accounting policies and the reported amounts or assets, liabilities, income and expenses. Actual results may differ from these estimates.
Estimates and underlying assumptions are reviewed on an ongoing basis. Revisions to accounting estimates are recognised in the period in which the estimate is revised and in any future periods affected. - Materiality and Aggregation
Each material class of similar items is presented separately in the financial statements. Items of a dissimilar nature or function are presented separately unless they are immaterial.
- Statement of Compliance
- SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
The financial statements of the Company are prepared in accordance with the SLFRS for SMEs issued by the Institute of Chartered Accountants of Sri Lanka. The principal accounting policies applied in the preparation of these financial statements are set out below. These policies have been consistently applied to all the years presented, unless otherwise stated.- Foreign Currency Transactions/Translation
Transactions in foreign currencies are translated to Sri Lankan Rupees at the foreign exchange rate rulings at the date of the transaction. Monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies as at the date of statement of financial position are translated to Sri Lankan Rupees at the foreign exchange rate ruling at that date. Foreign exchange differences arising on translation are recognised in the profit or loss. Non-monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies, which are stated at historical cost, are translated to Sri Lankan Rupees at the foreign exchange rate ruling at the date of the transaction. - Income Tax Expense
The tax expense for the period comprises current and deferred tax. Tax is recognised in profit or loss, except that a change attributable to an item of income or expense recognised as other comprehensive income is also recognised directly in other comprehensive income.- (a) Current Tax
Current tax is the expected tax payable on the taxable income for the year, using tax rates enacted or substantively enacted at the reporting date and any adjustment to tax payable in respect of previous years.
The Company’s liability to tax has been computed in accordance with the provisions of the Inland Revenue Act, No. 24 of 2017 and subsequent amendments thereto. - Deferred Tax
Deferred tax is recognised on differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities in the financial statements and their corresponding tax bases (known as temporary differences). Deferred tax liabilities are recognised for all temporary differences that are expected to increase taxable profit in the future. Deferred tax assets are recognised for all temporary differences that are expected to reduce taxable profit in the future and any unused tax losses or unused tax credits. Deferred tax assets are measured at the highest amount that, on the basis of current or estimated future taxable profit, is more likely than not to be recovered.
The carrying amount of deferred tax is reviewed at each reporting date and is adjusted to reflect the current assessment of future taxable profits. Any adjustments are recognised in profit or loss.
Deferred tax is calculated at the tax rates that are expected to apply to the taxable profit (tax loss) of the periods in which it expects the deferred tax asset to be realised or the deferred tax liability to be settled, on the basis of tax rates that have been enacted or substantively enacted by the end of the reporting period.
ASSETS AND BASES OF VALUATION
Assets classified as current assets in the statement of financial position are cash and those which are expected to be realised in cash during the normal operating cycle of the Company’s business or within one year from the reporting date whichever is shorter. Assets other than current assets are those which the Company intends to hold beyond a period of one year from the date of financial position.
- (a) Current Tax
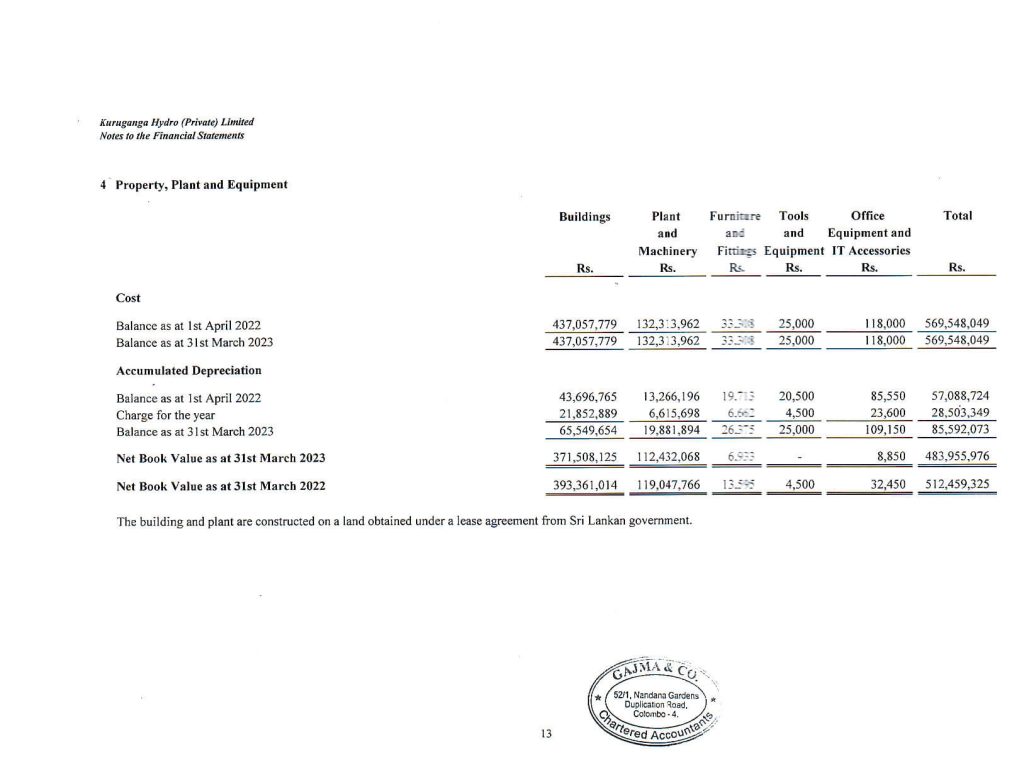
- Property, Plant and Equipment
- Recognition and Measurement
Items of property, plant and equipment are stated at cost or deemed cost less accumulated depreciation and any accumulated impairment losses (except which was carried at revalued amount in the statement of financial position). Historical cost includes expenditure that is directly attributable to bringing the asset to the location and condition necessary for it to be capable of operating in the manner intended by the management. The cost of self-constructed assets includes the cost of materials and direct labour.
Where an item of property, plant and equipment comprises major components having different useful lives, they are accounted for as separate items of property, plant and equipment. - Subsequent Expenditure
The Company adds to the carrying amount of an item of property, plant and equipment, the cost of replacing parts of such an item, when that cost is incurred if the replacement part is expected to provide incremental future benefits to the Company. The carrying amount of the replaced part is derecognised. All other repairs and maintenance are charged to profit or loss during the period in which they are incurred. - Depreciation
Depreciation is charged to the profit or loss so as to allocate the cost of assets less their residual value over the estimated useful lives of items of property, plant and equipment, using the straight-line method. The estimated annual rates are as follows.
- Recognition and Measurement
- Foreign Currency Transactions/Translation
| Assets | Annual Rates |
| Building | 5% |
| Plant and Machinery | 5% |
| Furniture and Fittings | 20% |
| Tools and Equipment | 20% |
| Office Equipment and IT Accessories | 20% |
Depreciation of an asset begins when it is available for use and ceases at the earlier of the date that the asset is classified as held for sale and the date that the asset is derecognized.
The assets’ residual values, useful lives and depreciation methods are reviewed, and adjusted prospectively if appropriate, if there is an indication of a significant change since the last reporting date.
On disposal, the difference between the net disposal proceeds and the carrying amount of the item sold is recognised in profit or loss and included in ‘other income’ or ‘other operating expenses’.
- Impairment of Non-Financial Assets
At each reporting date, non-financial assets are reviewed to determine whether there is any indication that those assets have suffered an impairment loss. if there is an indication of possible impairment, the recoverable amount of any affected asset (or group of related assets) is estimated and compared with its carrying amount. If the estimated recoverable amount is lower, the carrying amount is reduced to its estimated recoverable amount and an impairment loss is recognised immediately in profit or loss.
If an impairment loss subsequently reverses, the carrying amount of the asset (or group of related assets) is increased to the revised estimate of its recoverable amount, but not in excess of the amount that would have been determined had no impairment loss been recognised for the asset (group of related assets) in prior years. A reversal of an impairment loss is recognised immediately in profit or loss. - Financial Instruments
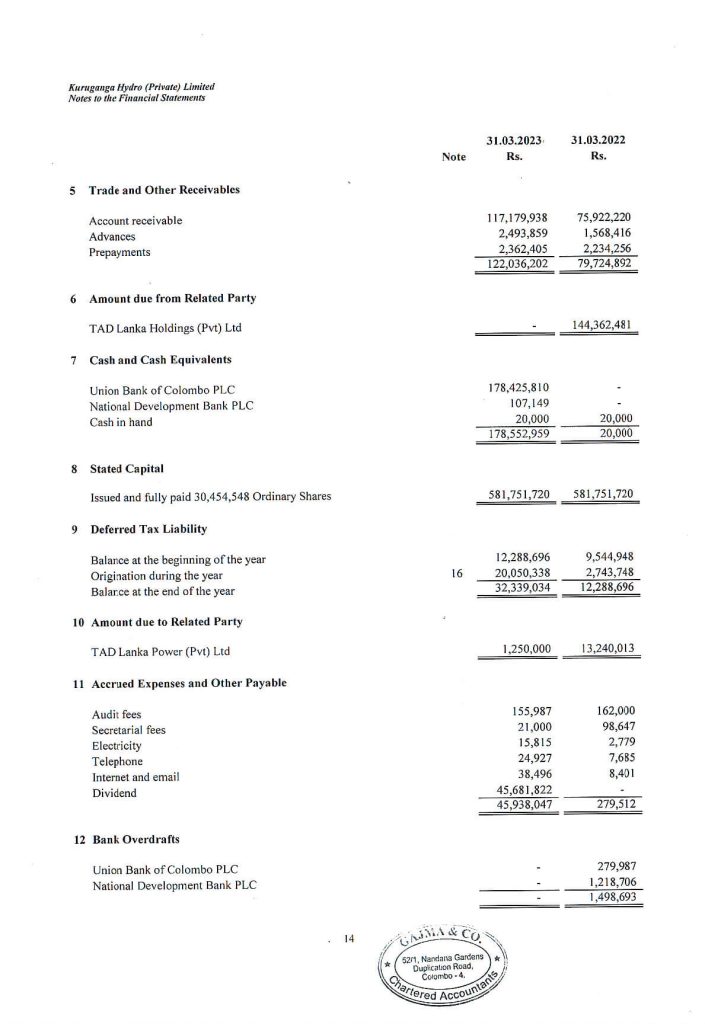
Financial Assets- 3.5.1 Trade and Other Receivables
Trade and other receivables are initially recognised at the transaction price. Most sales are made on the basis of normal credit terms, where the receivables do not bear interest and valued at undiscounted amount of cash receivable. Where credit is extended beyond normal credit terms, receivables are measured at amortised cost using the effective interest method. At the end of each reporting period, the carrying amounts of trade and other receivables are reviewed to determine whether there is any objective evidence that the amounts are not recoverable. If so, an impairment loss is recognised immediately in profit or loss. - Impairment of Financial Assets
At the end of each reporting period, the carrying amounts of financial assets that are not measured at fair value are reviewed to determine whether there is any objective evidence of impairment. If so, an impairment loss is recognised immediately in profit or loss and the carrying amount of financial asset is reduced accordingly. - Cash and Cash Equivalents
- Cash and cash equivalents include cash in hand, demand deposits and other short-term highly liquid investments with original maturities of three months or less. Bank overdrafts are shown in current liabilities on the statement of financial position.
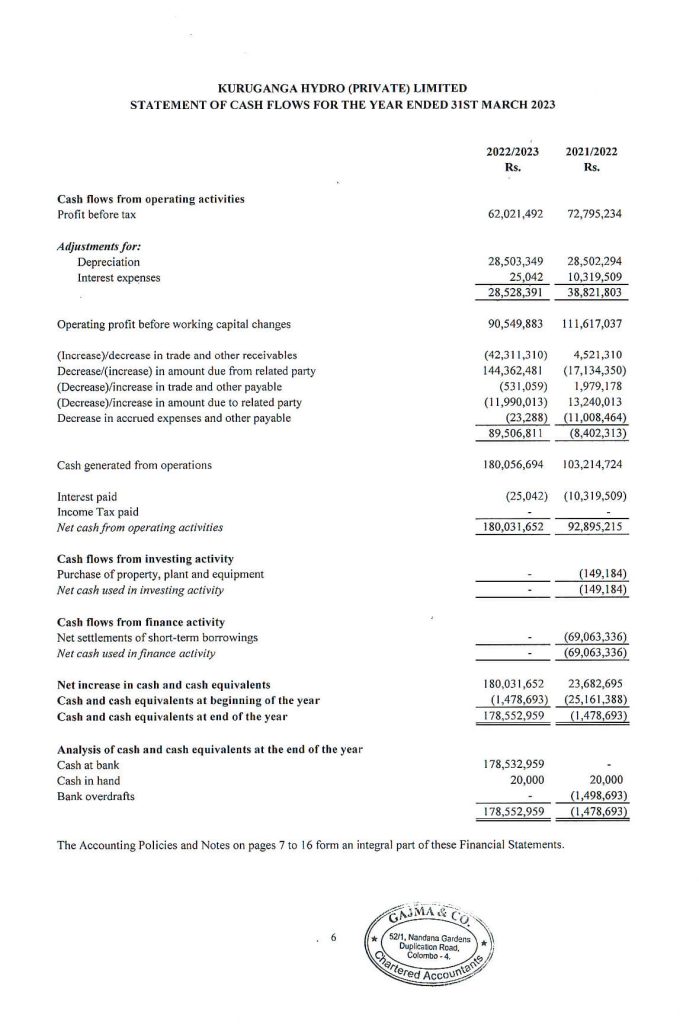
The statement of cash flows has been prepared by using the “Indirect Method”.
Financial Liabilities - Trade and Other Payable
Trade and other payables are initially recognised at the transaction price (including transaction costs). Trade payables are obligations on the basis of normal credit terms and do not bear interest. Interest bearing liabilities are subsequently measured at amortised cost using the effective interest method. - Bank Overdrafts
Overdrafts are repayable in full on demand and are initially measured and subsequently stated at face value.
LIABILITIES AND PROVISIONS
Liabilities classified as current liabilities on the statement of financial position are those which fall due for payment on demand or within one year from the reporting date. Non-current liabilities are those balances that fall due for payment after one year from the reporting date.
All known liabilities have been accounted for in preparing these financial statements. Provisions and liabilities are recognised when the Company has a legal or constructive obligation as a result of past events and it is probable that an outflow of economic benefits will be required to settle the obligation. - Contingencies and Capital Commitments
All material capital commitments and contingencies, which exist as at the reporting date, are disclosed in the respective notes to the financial statements.
STATEMENT OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME - Revenue Recognition
Revenue is recognised to the extent that it is probable that economic benefits will flow to the company and the revenue and associated cost incurred or to be incurred can be reliably measure, Revenue is measured at the fair value of the consideration received or receivable.
All expenditure incurred in the running of the business and in maintaining the property, plant and equipment in a state of efficiency has been charged to revenue in arriving at the profit or loss for the year.
- 3.5.1 Trade and Other Receivables